The five fundamentals of accounting are:
- Revenue recognition principles
- Cost principles
- Matching principles
- Full disclosure principles
- Objectivity principles
In today's business world, each industry has its language i.e., way of communicating. Accounting is the primary language of finance and related businesses. It helps business owners figure out financial situations by analysing important financial data. This information then turns the fundamentals of accounting into a comprehensive tangible report.
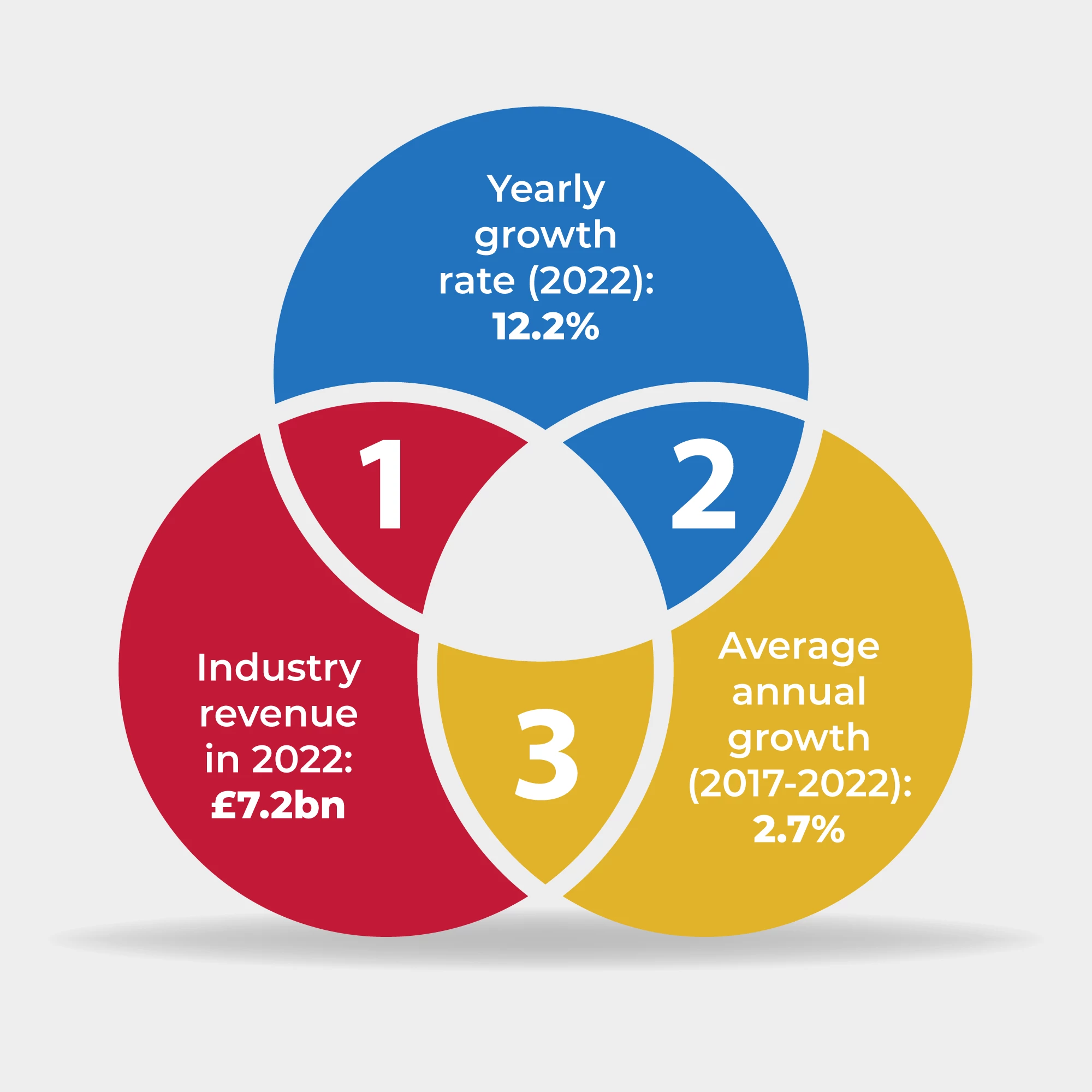
In 2022, the accounting & auditing industry made £7.2bn. That's a 12.2% increase from before. From 2017 to 2022, this industry in the UK grew by 2.7% each year.
Learning the fundamentals of accounting is really important for business owners and those just starting.
This blog is part of our guide on accounting. It explains why accounting matters, helps you learn the fundamentals of accounting and how accounting courses in the UK can help you achieve your goals. Let's dive in!
To get a grip on the fundamentals of accounting, you need to know what accounting means.
Accounting is all about organising a company's financial transactions in a structured manner. It includes keeping records, filing reports and processing and analysing financial transactions when needed. Accounting is essential for legal and tax reasons and to judge how well a business is doing. Every business transaction is accounted for. So, if you ever need information about expenses, it's easy to find.
|
|
There are eight main types of accounting: |
|
1. Financial accounting |
This kind of accounting makes sure transactions are shown properly in financial documents like income statements. These statements are shared with people outside the business. |
|
2. Management accounting |
This type of accounting makes financial information available to the management team. They use this information, such as budget details, to make important decisions in order to keep the business running smoothly. It’s an internal process that helps improve the overall business. |
|
3. Cost accounting |
This falls under the umbrella of management accounting, focusing on a company's expenses related to running its operations. It considers different costs such as fixed and variable costs, covering aspects like rent for business space, expenses for materials and the costs associated with labour. |
|
4. Tax accounting |
This is an accounting system primarily concerned with taxes. Instead of creating public financial statements, it focuses on preparing tax returns, analysing them and presenting tax payments accurately. |
|
5. Auditing |
Auditing offers an independent analysis of a company's financial activity. Its objective tracking and reporting systems ensure the business complies with applicable rules and best standards. Audits can be internal or external. Internal audits aim to assess the efficiency of a company's accounting methods, by identifying potential resource wastage and minimising the risk of fraud. They are necessary for the improvement of financial planning. External audits review a company's official financial statements to confirm their compliance with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). |
|
6. Forensic accounting |
This system investigates inconsistencies and fraudulent actions, using a mix of auditing, accounting and investigative expertise to scrutinise and understand business data. Forensic accountants are often used in legal cases to investigate fraudulent behaviour. Their services are extensively relied upon by accounting firms, law firms, banks, government agencies and insurance companies. |
|
7. Governmental accounting |
This type of accounting focuses on the financial activities of government bodies. Its main purpose is to guarantee transparency and responsibility in the management of public funds. |
|
8. International accounting |
As companies grow internationally, they encounter various accounting standards and methods which are unique to each country. Additionally, they need to consider currency exchange variations and global tax matters. International accounting deals specifically with applying specific accounting standards to a company's finances abroad. Activities include monitoring tax regulations and accounting principles that impact business transactions or activities. |
Accounting courses in the UK can help you gain an in-depth understanding of the different types of accounting.
There are five important fundamentals of accounting. These are the revenue recognition principles, cost principles, matching principles, full disclosure principles and objectivity principles.
This principle states that businesses should record their revenue at the time it is created. This is crucial because it shows the real financial situation of the company. This helps stakeholders make better decisions. Also, it ensures that companies follow the rules of GAAP and stay within legal boundaries.
Fundamentals of accounting: Common terminologies used and their definitions
Want to know more about the above terminologies? Pursue accounting courses in the UK and stay ahead of the industry.

The cost principle states that when a business deals with a financial transaction, it should be recorded at the original price. This cost is set when the transaction is completed which does not change even with the changing circumstances. This principle applies to all business assets, like land or equipment. A record is kept of a business’s tangible assets, without considering market value or depreciation. Following the cost principle requires the business to record its assets and liabilities and makes this simple to do.
It also gives solid proof of transactions, like sales receipts, invoices and bank reconciliation, making the financial position clear and accurate.
Fundamentals of accounting: Common terminologies used and their definitions
Pursue accounting courses in the UK from a reputed higher education institution and understand more about the basics of accounting.
The matching principle states that the expenses a business disburses should be recorded at the same time as the revenue generated. This means expenses should be recorded in the same period as the associated revenue and not at the time they are billed. This principle ensures that profits are shown accurately and truly reflect the real performance of the business. It also prevents expenses from being represented as being higher in one accounting period to offset revenue from a previous accounting period.
Fundamentals of accounting: Common terminologies used and their definitions
If you want to gain a deeper understanding of the fundamentals of accounting, pursue accounting courses in the UK. GBS offers “BSc (Hons) Accounting & Financial Management” for students who want to build a successful career in accounting and financial management.

The full disclosure principle in accounting states that important financial information must be shared with all stakeholders and owners, regardless of the nature of the information. This information must be disclosed accurately and on time. It includes details about assets, income, liabilities, expenses and other important financial indicators. This information may be reflected in public company filings, inventory valuation, or depreciation.
But when it comes to internally generated financial statements, this principle doesn't always apply. It's assumed that the management already has full knowledge of the business. Also, a business might choose to share only the information that affects the financial position of the business.
Fundamentals of accounting: Common terminologies used and their definitions
Study accounting courses in the UK to learn the fundamentals of accounting and make a strong foundation for your career ahead in the industry.
The objectivity principle in accounting states that financial statements should be prepared based on objective evidence and only show the facts. Following this principle ensures that the statements are correct, fair and free from bias. This prevents an accountant or bookkeeper from changing financial statements based on what they estimate or on rumours. If there are any changes made to the statement, they need to clearly document those changes. This is a fundamental principle of GAAP.
Fundamentals of accounting: Common terminologies used and their definitions
If you're interested in becoming an accountant and learning the fundamentals of accounting, it's recommended to get some form of formal education like pursuing accounting courses in the UK. A proper education covers everything you need to know. Self-study or working as an assistant to an accountant might leave some knowledge gaps and make it hard to do the job well.
At GBS, you can pursue an accounting course in the UK, BSc (Hons) Accounting & Financial Management.
GBS is a leading higher education institution in the UK known for its industry-specific courses in areas such as finance, business, education, healthcare and more. With a wide presence in the major cities of the UK, the institution is dedicated to its mission of “changing lives through education.”
The BSc (Hons) Accounting & Financial Management degree is a four-year course that includes a foundation year. You can take this course at different GBS campuses such as in London, Birmingham, Leeds and Manchester.
Whether you're aiming for a career in accounting and financial management or dreaming of starting your own business, understanding numbers is crucial for success. This accounting course in the UK teaches you the latest principles, theories and practical skills in the exciting field of accounting and financial management.
This degree in accounting and financial management provides you with the essential knowledge and skills needed for a successful career that aligns with your goals.
1. What are the five fundamentals of accounting?
The five fundamentals of accounting are:
2. What are the basics of accounting?
Simply put, fundamental accounting keeps track of cash movements and business activities. It categorises all transactions into debits and credits.
3. What are liabilities in accounting?
In accounting, liability refers to any financial obligation a business owes to an individual or another business by the end of an accounting period. These obligations are cleared by transferring economic assets like money, goods, or services.
4. Who is the father of the fundamentals of accounting?
Italian, Luca Pacioli is recognised as the pioneer of modern accounting. In 1494, he detailed the double-entry bookkeeping method employed by Venetian merchants in his work, Summa de Arithmetica, Geometria, Proportioni et Proportionalita. Although not the originator of the method, Pacioli was the first to articulate the concept of debits and credits in journals and ledgers, forming the foundation of contemporary accounting systems that we use today.
5. How can I learn the fundamentals of accounting?
Learning the fundamentals of accounting is essential for all finance experts as it provides a valuable understanding of profits, operations, expansion and the fundamental factors driving the business. You can gain a deep knowledge of accounting by pursuing an accounting course in the UK with GBS. Its BSc (Hons) Accounting & Financial Management degree can help you achieve your dream of succeeding in the industry.